When exploring loan options, borrowers are bombarded with options. 😵💫 One such option is a straight loan, also called a term loan.
Nowadays, conventional loans are the most common type of loan to apply for, but ironically enough, before the mortgage crisis of the 1930’s that led to more than 50% of mortgages going into foreclosure, a straight loan was the loan to get. Default rates were low and borrowers felt confident they could pay back their loans at the end of the term. Who knew? 🤷
Now, borrowers understand that stock prices, real estate, valuable metals, and other investable assets don't increase indefinitely. Paying down debt over the course of a loan term has become more popular because it can reduce financial risk.
However, many individuals and businesses still use straight loans today for small and big investments. 💸 Let’s explore the details of these loans, including how they differ from other types of loans and what you should know before applying for one of your own.
TL;DR:
- Straight loans (aka term loans), explained
- Straight loans vs. other types of loans
- Features and uses of a straight loan
- What to know before applying for one
Is a straight loan the same thing as a term loan? And what does it mean?

Did you know? Term loans are a more common way to refer to straight loans, but they mean the same thing. They’re also called interest-only loans and straight term mortgages. Financial jargon can be overwhelming, but don’t let this simple switch cause confusion! All four terms are the same type of loan! 😅
Straight loans are immediate-, short-, or long-term loans in which the borrower only pays down the interest for the majority of the loan. They don’t make payments on the principal (the amount they borrowed) until the end of the loan period, they make interest payments, making this a non-amortized loan. At the end of the loan period, a borrower may choose to refinance the loan or pay off the loan amount.
In contrast, amortization occurs when a borrower gradually pays off a loan principal over a period of time. ⏰
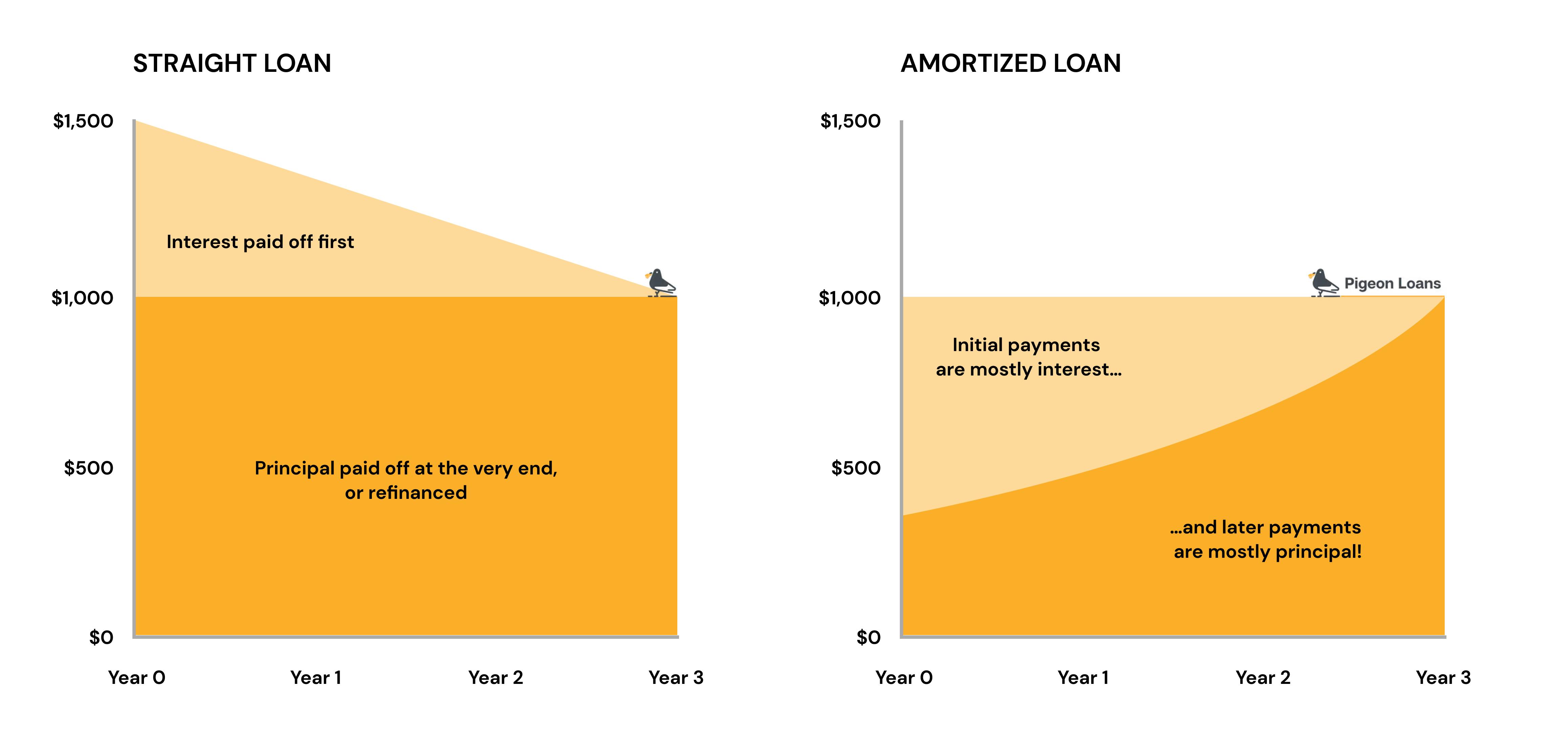
Straight loans fall under the category of special purpose loans: they can be used for business purposes or personal investments. In the early days of mortgages, straight loans were the main type of loan. Today, borrowers typically use them for buying land, financing construction projects, or investing in small business equipment and property.
When is a good time to take out a straight loan?
A straight loan comes in handy when a borrower requires a lump sum of cash upfront without the requirement to pay off the loan right away. Interest-only loans like this allow for lower payments over the life of the loan. If the borrower uses the loan to invest in something, like land or equipment, they can use any proceeds made on the investment to pay off the loan balance with a full loan repayment at the end.
For business term loans, you will likely need a credit score of at least 600 to qualify. Other factors, like time in business (typically at least one year) and annual revenue (typically at least $100,000), may impact your approval. Personal straight loans may also require a credit score of at least 600 and a low debt-to-income (DTI) ratio of 35% or less.

Features of a straight loan and when you might use one
We’ve defined straight loans somewhat so far—now let’s dig into them a little more.👇🏽
When you sign a contract for a straight loan, you’re agreeing to pay the interest on the loan on a regular basis. Your installment frequency depends on the agreement, but monthly payments are one of the most common options. These payments continue for the full term of the loan in a non-amortization process and often include a fixed interest rate. At the end of the term, you’re usually expected to pay off the entire principal in a single payment.
If you cannot pay off your principal, you may have the option to refinance the loan, either as another straight loan or a different type of loan altogether.
How straight loans differ from other types of loans
Straight loans are an alternative type of loan. Other loan types include:
- Conventional loans: These differ from straight loans in that borrowers pay a down payment and then pay down the loan principal over time (the amortization process described above). Typical home equity loans fall under this category. 🏡 On the contrary, straight loans are interest-only until the end of the loan term.
- Government-backed loans: In the US, the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) insures certain long-term mortgage loans. VA loans guarantee loans to qualified US military veterans. The US Department of Agriculture (USDA) offers loans through its Rural Development program to help people in rural areas buy homes with no down payment and make other investments. Additionally, the Small Business Administration (SBA) has programs in place to link small business owners with loans from third-party lenders. These differ from straight loans in that they amortize. They also come from a federal source, which often means favorable loan conditions.
- Seller financing: In the case of mortgage loans, seller financing refers to home sellers financing the loan for the buyer. Straight loans typically go through an official lender or investor, but could potentially go through a seller as well.
There are also other types of special-purpose loans. Open-ended loans, buy-down mortgages, adjustable-rate mortgages, graduated payments mortgages, balloon mortgages, package loans, and more make up this category. All—including straight loans—are unique.
What to know before applying for a straight loan

Some long-term straight loans may not require balloon payments (AKA large, one-time payments) toward the end of a loan term. They may instead spread out the principal payment over multiple installments. However, immediate- and short-term straight loans often do require a balloon payment at the end. 🎈🔚
For long-term straight loans, you may also have to provide collateral (or something of value backing the loan). This is typically a physical asset like a house.
Straight loans often come with lower interest rates than other types of loans. However, they may carry a fixed or variable interest rate. If it’s a variable interest rate, payments could be much higher than they were when you first took out the loan. This can make your loan or mortgage payments pricier than you can afford. Be careful with variable interest rate loans.
If you’re taking out a straight loan to invest in a construction development or another project that you expect will generate income down the line, make sure you have the option to refinance the straight loan at the end of the term. You don’t want to get caught with a balloon payment you can’t afford if the project lags or fails.
You can use a straight loan for any purpose, and you don’t necessarily need to go through a traditional lender to get one. For a non-traditional route, Pigeon is a great option for people to lend money to friends and family. 🐣 The lender and borrower negotiate the loan’s terms themselves (including a straight loan, if that option works best for all parties). Pigeon provides all documentation, stores signed copies, and sends out payment reminders as the due dates come. You can even set custom terms, like origination fees and prepayment penalties, if applicable. 💯
To recap:
Straight loans (or term loans) are a way for borrowers to get low-interest loans without having to pay off the principal right away. Business owners, individuals, and hopeful homeowners may utilize straight loans to buy equipment, purchase land, fund construction projects, or make other investments.
There are nuances to be aware of before taking out a straight loan. Sift through your options to determine which loan type works best for your situation and will help you thrive in work and life. 🤸🏾♀️

Want to read more related content? Check out some more of our awesome educational pieces below:




